What is the difference between sea ice and glaciers?
Sea ice forms and melts strictly in the ocean whereas glaciers are formed on land.
 
Icebergs are chunks of glacial ice that break off glaciers and fall into the ocean.
- When glaciers melt,
because that water is stored on land,
the runoff significantly increases the amount of water in the ocean,
contributing to global sea level rise.
- Sea ice, on the other hand,
is often compared to ice cubes in a glass of water:
when it melts, it does not directly change the level of water in the glass.
Instead, depleting Arctic sea ice triggers a host of other devastating consequences
—from depleting available ice on which walrus can haul out
or polar bears hunt to changing weather systems around the world
by altering the pattern of the Jet stream.
What are the effects of melting glaciers on sea level rise?
Melting glaciers add to rising sea levels,
which in turn increases coastal erosion
and elevates storm surge as warming air
and ocean temperatures create more frequent
and intense coastal storms like hurricanes and typhoons.
Specifically, the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets
are the largest contributors of global sea level rise.
Right now, the Greenland ice sheet is disappearing four times faster than in 2003
and already contributes 20% of current sea level rise.
How much and how quickly these Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets melt in the future
will largely determine how much ocean levels rise in the future.
If emissions continue to rise,
the current rate of melting on the Greenland ice sheet is expected to double by the end of the century.
Alarmingly, if all the ice on Greenland melted, it would raise global sea levels by 20 feet.
How do melting sea ice and glaciers affect weather patterns?
Today, the Arctic is warming twice as fast as anywhere on earth,
and the sea ice there is declining by more than 10% every 10 years.
As this ice melts, darker patches of ocean start to emerge,
eliminating the effect that previously cooled the poles,
creating warmer air temperatures
and in turn disrupting normal patterns of ocean circulation.
Research shows the polar vortex is appearing outside of the Arctic more frequently
because of changes to the jet stream,
caused by a combination of warming air and ocean temperatures in the Arctic and the tropics.
The glacial melt we are witnessing today in Antarctic and Greenland
is changing the circulation of the Atlantic Ocean
and has been linked to collapse of fisheries in the Gulf of Maine
and more destructive storms and hurricanes around the planet.
Even if we significantly curb emissions in the coming decades,
more than a third of the world’s remaining glaciers will melt before the year 2100.
When it comes to sea ice, 95% of the oldest and thickest ice in the Arctic is already gone.
What are the effects of melting glaciers and sea ice loss on humans and wildlife?
What happens in these places has consequences across the entire globe.
As sea ice and glaciers melt and oceans warm,
ocean currents will continue to disrupt weather patterns worldwide.
Industries that thrive on vibrant fisheries
will be affected as warmer waters change where and when fish spawn.
Coastal communities will continue to face billion-dollar disaster recovery bills as flooding
becomes more frequent and storms become more intense.
People are not the only ones impacted.
In the Arctic, as sea ice melts,
wildlife like walrus are losing their home and polar bears are spending more time on land,
causing higher rates of conflict between people and bears.
|
Warming temperatures and loss of oxygen in the sea
will shrink hundreds of fish species
—from tunas and groupers to salmon, thresher sharks, haddock and cod—
even more than previously thought, a new study concludes.
Because warmer seas speed up their metabolisms,
fish, squid and other water-breathing creatures
will need to draw more oxyen from the ocean.
At the same time, warming seas are already reducing
the availability of oxygen in many parts of the sea.
Since the bodies of fish grow faster than their gills,
these animals eventually will reach a point
where they can't get enough oxygen to sustain normal growth.
"What we found was that the body size of fish decreases by 20 to 30 perent
for every 1 degree Celsius increase in water temperature,"
says author William Cheung, director of science for the university's Nippon Foundation.
These changes, the scientists say, will have a profound impact on many marine food webs,
upending predator-prey relationships in ways that are hard to predict.
(Read about how climate change is resulting in smaller mountain goats.)


 
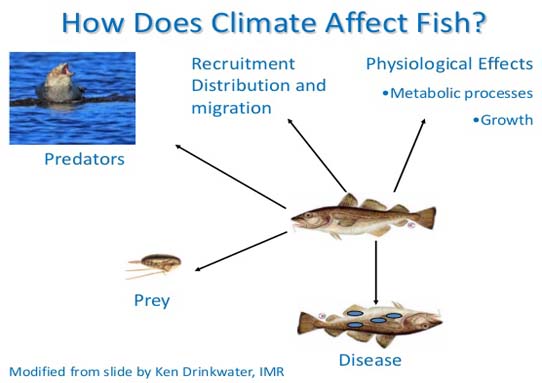
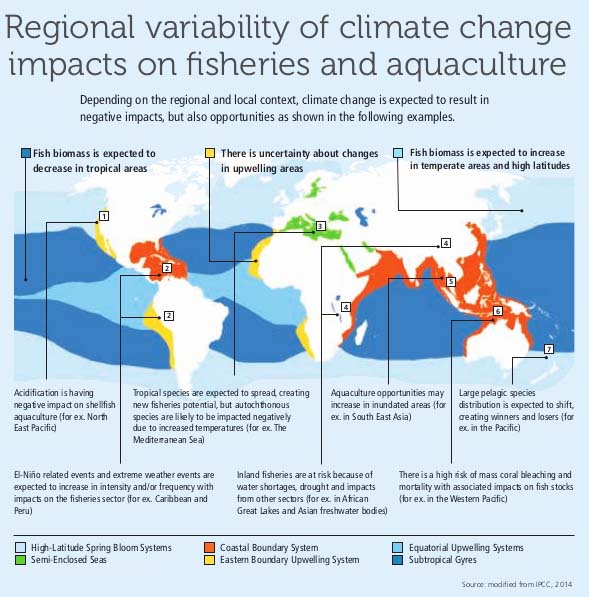
 schematic representations of impacts of climate change and fishing activity on
the marine ecosystem and its fish component.
schematic representations of impacts of climate change and fishing activity on
the marine ecosystem and its fish component.
|



 ภัยคุกคามที่ทวีคูณ
สำหรับสัตว์ทะเล น้ำทะเลที่มีออกซิเจนน้อยทำให้ระบบสืบพันธุ์อ่อนแอ อายุขัยสั้น และเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรม
แม้แต่การอยู่ในน้ำทะเลออกซิเจนต่ำเพียงชั่วครู่ก็ทำให้ระบบภูมิคุ้มกันเปลี่ยนแปลงไป และเป็นโรคง่ายขึ้น
น้ำทะเลออกซิเจนต่ำยังส่งผลต่อสัตว์ทะเลรุ่นถัดๆ ไปในอนาคต
ด้วยการเปลี่ยนการแสดงออกทางพันธุกรรม (gene expression) ในปลาและสัตว์ทะเลอื่นๆ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงดังกล่าวทำให้ปลาต่างๆ ตั้งแต่ทูนา ฉลาม เฮอร์ริง แชด แมกเคอเรล ค็อตแปซิฟิก และกระโทงดาบ
ต้องพากันไปอยู่ในบริเวณแถบน้ำที่มีออกซิเจนมากแถบแคบๆ บริเวณผิวน้ำ
พอสัตว์น้ำเหล่านี้มาอยู่รวมกันมากเข้า สัตว์ผู้ล่าผิวน้ำเช่นเต่า นก และอื่นๆ รวมทั้งกองทัพเรือประมงด้วย
ทีมวิจัยของเบรตเบิร์กยังพบด้วยว่าการสูญเสียออกซิเจน
ส่งผลกระบทบกับเขตที่มีการพัดพาสารอาหารจากกระแสน้ำเย็นขึ้นมายังผิวน้ำ
เช่น เขตชายฝั่งตะวันตกของสหรัฐอเมริกาและอเมริกาใต้
การที่น้ำอุ่นขึ้นไม่เพียงแต่เพิ่มการพัดพาสารอาหารขึ้นเท่านั้น
แต่ยังนำน้ำที่มีออกซิเจนต่ำขึ้นสู่พื้นผิวอีกด้วย
ในออริกอนตอนกลาง กระบวนการนี้ทำให้เกิดเขตมรณะใหม่ๆ ขึ้นด้วย
ภัยคุกคามที่ทวีคูณ
สำหรับสัตว์ทะเล น้ำทะเลที่มีออกซิเจนน้อยทำให้ระบบสืบพันธุ์อ่อนแอ อายุขัยสั้น และเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรม
แม้แต่การอยู่ในน้ำทะเลออกซิเจนต่ำเพียงชั่วครู่ก็ทำให้ระบบภูมิคุ้มกันเปลี่ยนแปลงไป และเป็นโรคง่ายขึ้น
น้ำทะเลออกซิเจนต่ำยังส่งผลต่อสัตว์ทะเลรุ่นถัดๆ ไปในอนาคต
ด้วยการเปลี่ยนการแสดงออกทางพันธุกรรม (gene expression) ในปลาและสัตว์ทะเลอื่นๆ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงดังกล่าวทำให้ปลาต่างๆ ตั้งแต่ทูนา ฉลาม เฮอร์ริง แชด แมกเคอเรล ค็อตแปซิฟิก และกระโทงดาบ
ต้องพากันไปอยู่ในบริเวณแถบน้ำที่มีออกซิเจนมากแถบแคบๆ บริเวณผิวน้ำ
พอสัตว์น้ำเหล่านี้มาอยู่รวมกันมากเข้า สัตว์ผู้ล่าผิวน้ำเช่นเต่า นก และอื่นๆ รวมทั้งกองทัพเรือประมงด้วย
ทีมวิจัยของเบรตเบิร์กยังพบด้วยว่าการสูญเสียออกซิเจน
ส่งผลกระบทบกับเขตที่มีการพัดพาสารอาหารจากกระแสน้ำเย็นขึ้นมายังผิวน้ำ
เช่น เขตชายฝั่งตะวันตกของสหรัฐอเมริกาและอเมริกาใต้
การที่น้ำอุ่นขึ้นไม่เพียงแต่เพิ่มการพัดพาสารอาหารขึ้นเท่านั้น
แต่ยังนำน้ำที่มีออกซิเจนต่ำขึ้นสู่พื้นผิวอีกด้วย
ในออริกอนตอนกลาง กระบวนการนี้ทำให้เกิดเขตมรณะใหม่ๆ ขึ้นด้วย