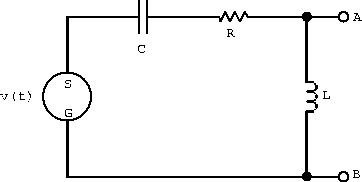
- What is the transfer function H(
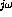 )?
)?
- Find the current in the circuit.
- What is the voltage drop across each element of the circuit?
- Show algebraically that at any instant the potential difference around the circuit is zero.
- At time
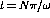 , where N=0,2,4,... make a sketch
showing the voltage across each element in the complex plane
and show that the vector sum of the voltage drops is equal to
the voltage supplied.
, where N=0,2,4,... make a sketch
showing the voltage across each element in the complex plane
and show that the vector sum of the voltage drops is equal to
the voltage supplied.
- Write an expression for
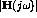 .
.
- What is the limit of
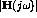 as
as  goes to
zero?
goes to
zero?
- What is the limit of
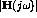 as
as  goes to
infinity?
goes to
infinity?
- What is the corner frequency?
- What is
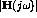 at the corner frequency?
at the corner frequency?
- Make a sketch showing the characteristics of
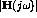 on a log-log plot. Label the slope of the curve
where possible, the corner frequency, and the value of
on a log-log plot. Label the slope of the curve
where possible, the corner frequency, and the value of 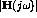 at the corner frequency.
at the corner frequency.
- Describe the high and low frequency behavior in dB/octave.
- Draw a passive LCR low-pass filter and write down the transfer function of your four-terminal network.
- Determine approximations to the transfer function and filter corner frequency(s).
- Write the resonance frequency,
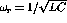 , in terms
of the corner frequency(s).
, in terms
of the corner frequency(s).
- the corner frequency(s) and
- the value(s) of
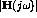 at the corner frequency(s).
at the corner frequency(s).
- Sketch
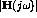 and the voltage phase-shift as a
function of
and the voltage phase-shift as a
function of  .
.
- What type of filter is this?
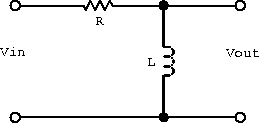
- What is the transfer function for the following circuit?
- Describe the frequency response at low and high frequencies?
- Sketch the magnitude
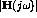 on a log-log plot.
(label slopes, the corner frequency(s), and
on a log-log plot.
(label slopes, the corner frequency(s), and 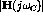 )
)
- What is the signal attenuation for
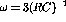 .
.
- Show that the transfer function of a single-pole RC filter drops by 3 db at the corner frequency. This is often refereed to as the 3 db down-point.
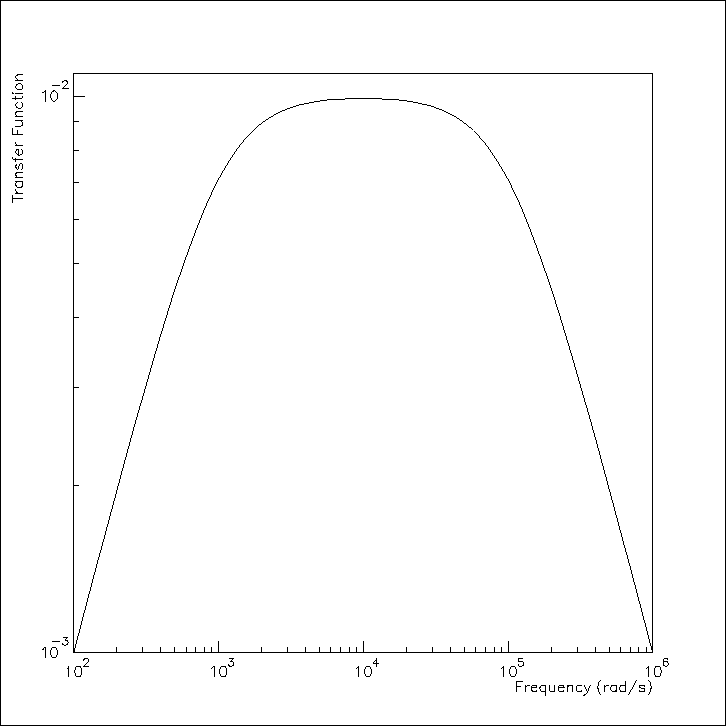
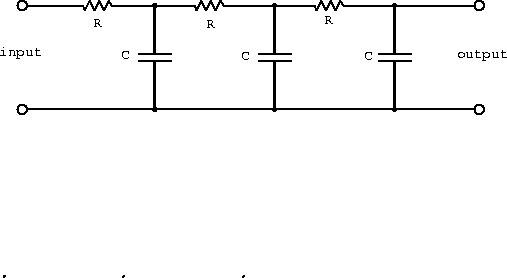
- Design a bandpass RC filter with the transfer function shown
below.
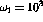 rad/s and
rad/s and 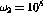 rad/s are the
3 db down-points of the RC filter sections. Choose impedances
so that the first section is not much affected by the loading of
the second section.
rad/s are the
3 db down-points of the RC filter sections. Choose impedances
so that the first section is not much affected by the loading of
the second section.
- Are
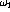 and
and 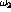 the 3 db down-points of a bandpass
filter?
the 3 db down-points of a bandpass
filter?